|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
|
|
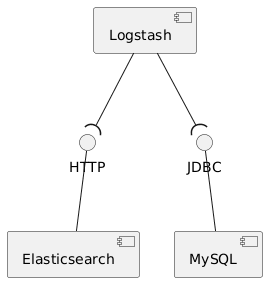
+This is an example how Elasticsearch can be synchronized with a MySQL database by using Logstash.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+# How it works
|
|
|
+The MySQL database stores `articles` in a table and every time an article gets inserted or updated, Logstash takes care
|
|
|
+of that the changes are synchronized to Elasticsearch.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+To keep them in sync, Logstash polls the MySQL instance every 5 seconds and checks the articles table for updates.
|
|
|
+The articles table has a `modifcation_time` column and Logstash tracks the last known value to query the updates (see
|
|
|
+[sync-pipeline.conf](logstash/sync-pipeline.conf)).
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+# Prerequisites
|
|
|
+* `docker` and `docker-compose`
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+# Getting started
|
|
|
+1. Execute `docker-compose up` to startup all components (MySQL, Elasticsearch and Logstash).
|
|
|
+1. Connect to the MySQL database and insert some articles (schema: `blog`, username: `blog`, password: `blog`).
|
|
|
+ ```
|
|
|
+ insert into articles (id, title, content) values ('1','first_title','first_content');
|
|
|
+ insert into articles (id, title, content) values ('2','second_title','second_content');
|
|
|
+ insert into articles (id, title, content) values ('3','third_title','third_content');
|
|
|
+ ```
|
|
|
+1. Query Elasticsearch and see the result.
|
|
|
+ ```
|
|
|
+ curl localhost:9200/articles/_search
|
|
|
+ ```
|
|
|
+1. Insert and update some articles in MySQL and query Elasticsearch afterwards to see the changes.
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+# Pitfalls
|
|
|
+* deleted articles in MySQL are still available in Elasticsearch
|
|
|
+* Logstash needs a JDBC driver to connect to the database
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+# Implementation details
|
|
|
+* [docker-compose.yml](docker-compose.yml) starts the example
|
|
|
+* [sync-pipeline.conf](logstash/sync-pipeline.conf) contains the Logstash pipeline config
|
|
|
+* [schema.sql](mysql/schema.sql) defines the database schema
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+# Further readings
|
|
|
+* https://www.elastic.co/blog/how-to-keep-elasticsearch-synchronized-with-a-relational-database-using-logstash
|