|
|
hace 6 años | |
|---|---|---|
| logstash | hace 6 años | |
| mysql | hace 6 años | |
| rdbc | hace 6 años | |
| .gitignore | hace 6 años | |
| README.md | hace 6 años | |
| docker-compose.yml | hace 6 años |
README.md
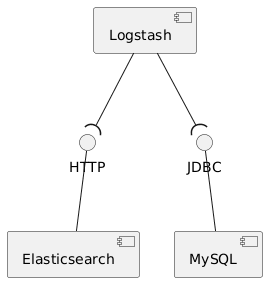
This is an example how Elasticsearch can be synchronized with a MySQL database by using Logstash.
How it works
The MySQL database stores articles in a table and every time an article gets inserted or updated, Logstash takes care
of that the changes are synchronized to Elasticsearch.
To keep them in sync, Logstash polls the MySQL instance every 5 seconds and checks the articles table for updates.
The articles table has a modifcation_time column and Logstash tracks the last known value to query the updates (see
sync-pipeline.conf).
Prerequisites
dockeranddocker-compose
Getting started
- Execute
docker-compose upto startup all components (MySQL, Elasticsearch and Logstash). Connect to the MySQL database and insert some articles (schema:
blog, username:blog, password:blog).insert into articles (id, title, content) values ('1','first_title','first_content'); insert into articles (id, title, content) values ('2','second_title','second_content'); insert into articles (id, title, content) values ('3','third_title','third_content');Query Elasticsearch and see the result.
curl localhost:9200/articles/_searchInsert and update some articles in MySQL and query Elasticsearch afterwards to see the changes.
Pitfalls
- deleted articles in MySQL are still available in Elasticsearch
- Logstash needs a JDBC driver to connect to the database
Implementation details
- docker-compose.yml starts the example
- sync-pipeline.conf contains the Logstash pipeline config
- schema.sql defines the database schema